ELECTROSTATIC PRECIPITATORS INSULATORS (ESP INSULATORS)
ESPI Europe is a global specialist in designing, manufacturing, and distributing insulators for electrostatic precipitators (ESP insulators).
Our portfolio consists of of support insulators, wall bushing insulators, shaft (rotary) insulators, solid-core post insulators, suspension insulators, rapping rods, stabilizers, anti-sway bars or dumping insulators.
What is an insulator for an electrostatic filter?
An insulator for an electrostatic filter, sometimes also called an electrostatic precipitator or electrofilter, is a special type of ceramic insulator made from highly resistant ceramic material. It is most commonly made from C130, C610 materials, or even from high-alumina porcelain with an alumina oxide (Al2O3) content of up to 95%.
What is the function of the insulator in an electrostatic precipitator?
Conical or cylindrical insulators for electrofilters insulate electrically charged electrodes from the body of the electrofilter. The electrodes are structurally attached to a suspension system, which is holds by the insulator. Therefore, the insulator must be extremely strong, resistant to high temperatures, and have perfect insulation properties. The specified compressive strength of an insulator for an electrostatic filter is usually 500 kN; tests have shown that one insulator can withstand even over 1,000 kN, i.e., over 100 tons. The insulator is usually exposed to an operating temperature of around 180°C, but filter manufacturers often require and insulator manufacturers provide temperature resistance up to 400°C. Insulators made of high-alumina porcelain offer thermal resistance up to 600°C.
What is an electrostatic filter and where is it used?
An electrostatic filter is a device using electrostatic energy that separates dust particles from polluted air or gas. Electrostatic filters are commonly used in industrial plants that produce waste gases. Typical applications include coal-fired power plants, cement plants, chemical plants, steel mills, and increasingly, biomass combustion plants.
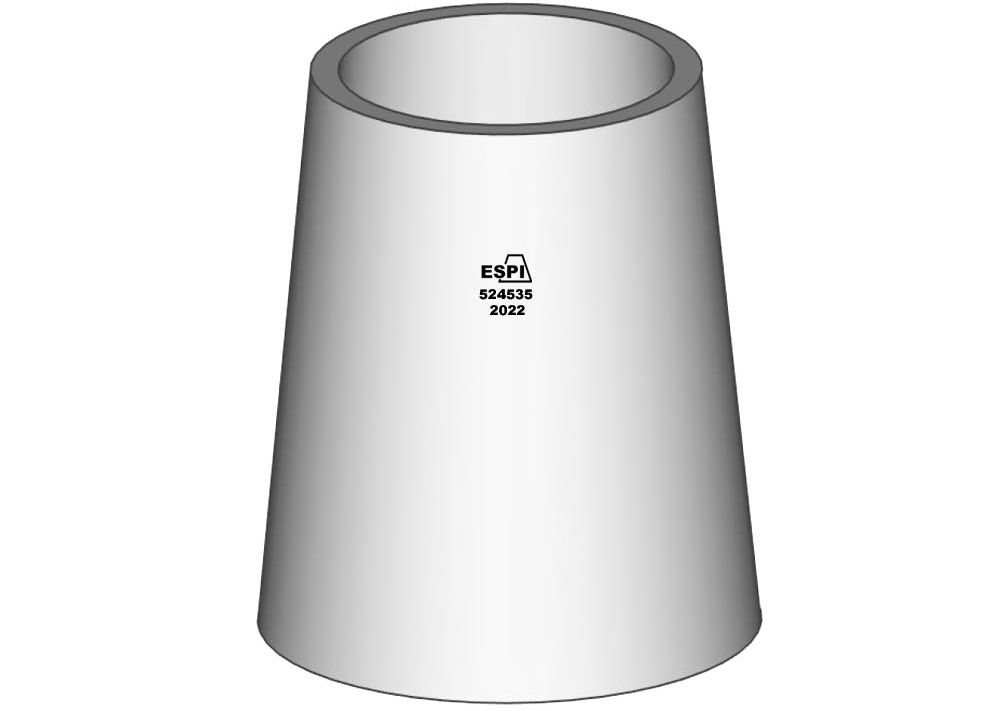

ESP SUPPORT INSULATORS
The purpose of the ESP support insulator is to support collecting plates, which are high-voltage positively charged electrodes, and to insulate them from the electrostatic precipitator housing. Support insulators can possess a cylindrical or conical shape and are crafted from ceramics that are resistant to high pressure and temperature.
ESP WALL BUSHING INSULATORS
The function of a wall bushing is to permit an electrical conductor to pass through a wall from the outside to the chamber. Bushing insulators can have a smooth surface body or various shapes depending on the required creepage distance.
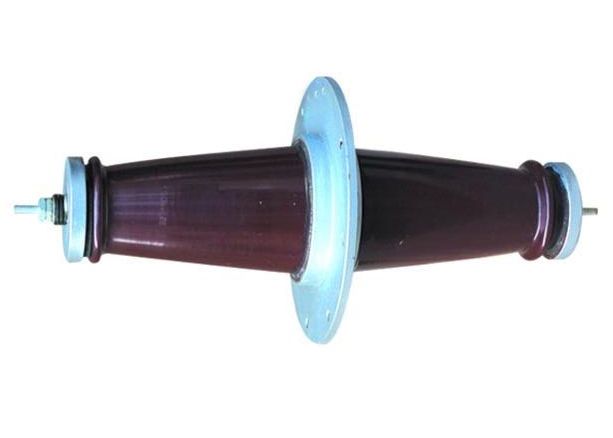


ESP SHAFT INSULATORS
The role of the shaft insulator within the ESP is to facilitate the rotation of the rod. This rod, in turn, initiates the movement of hammers that gently tap the collecting electrodes within the electrostatic precipitator. This tapping action serves to dislodge dust from the electrodes, effectively cleaning them.
ESP DAMPING RESISTANCE INSULATORS
Damping resistance insulators play a crucial role in absorbing the higher harmonic components present in the secondary circuit of the rectifier transformer. This absorption helps prevent resonance within the output circuit, subsequently safeguarding the rectifier transformer. To achieve this protection, damping resistors should be installed at the output terminal of the rectifier transformer.

ESP HIGH ALUMINA INSULATORS
High alumina insulators are crafted from materials containing a substantial 95% proportion of Al2O3. These insulators are particularly well-suited for use in electrostatic filters operating at elevated temperatures, reaching up to 500 degrees Celsius. They exhibit an enhanced capacity to endure thermal shocks and boast remarkable mechanical strength. Typically, their surface remains unglazed.
Using high alumina material, a diverse range of insulators can be manufactured, including support insulators, wall bushings, shaft insulators, rapping rods, stabilizers, and anti-sway bars.
